Coordinate Systems
There are several different coordinate systems used in the documentation and code. This page illustrates the configuration of each, and
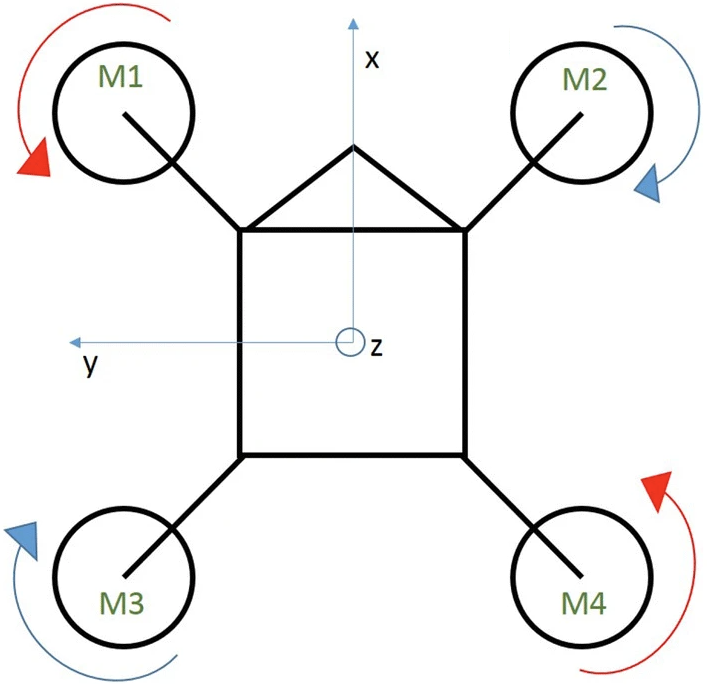
The Body Frame
The body frame is centered at the center of mass of the quadcopter.
X points ‘forward’
Y points ‘right’
Z points ‘up’
See the diagram below for an illustration
Euler Angles
The commonly used euler angles Roll, Pitch and Yaw describe the orientation of the body frame with respect to the horizon plane. That is, the plane incident to the drone’s center of mass and perpendicular to gravity. These are:
Roll: The angle (in radians) of the Body Frame’s X axis WRT the horizon plane
Pitch: The angle (in radians) of the Body Frame’s Y axis WRT the horizon plane
Yaw: The angle (in radians) of the Body Frame’s Z axis WRT it’s starting position. This measurement isn’t well defined, as the 2D horizon plane does not have ‘zero’ orientation for the Z axis
The IMU Frame
The IMU frame is simply the frame that the IMU is mounted to. It is important that the rotation matrix config parameter
R_imu_body is set properly so that the control loop can calculate coordinate system transformations correctly